Python遍历文件夹如何利用,由于Python语法简洁,所以用到的代码非常非常少,需要遍历一个文件夹下的所有文件也是超简单的,那么Python遍历文件夹如何利用呢?
Python遍历文件夹如何利用1
方法一:利用函数os.walk()来实现遍历文件夹
os.walk函数的定义:返回三元元组dirpath:根路径 (字符串),dirnames路径下的所有目录名(列表),filenames路径下的所有非目录文件名(列表))。
其中目录名和文件名都是没有加上根路径的',所以需要完整路径时需要将目录名或文件名与根路径连接起来。
如下代码所示:
importos root="C:\dir" fordirpath,dirnames,filenamesinos.walk(root): forfilepathinfilenames: printos.path.join(dirpath,filepath)
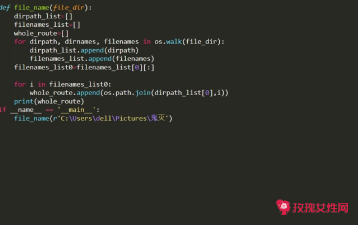
方法二:利用函数os.listdir(),os.path.isdir(),os.path.isfile()
os.listdir() 可以列出路径下所有文件和目录名,但是不包括当前目录., 上级目录.. 以及子目录下的文件.
os.path.isfile() 和 os.path.isdir() 判断当前路径是否为文件或目录
示例 :
importos deflistDir(rootDir): forfilenameinos.listdir(rootDir): pathname=os.path.join(rootDir,filename) if(os.path.isfile(filename)): printpathname else: listDir(pathname)
Python遍历文件夹如何利用2
在读文件的时候往往需要遍历文件夹,python的os.path包含了很多文件、文件夹操作的方法。下面列出:
os.path.abspath(path) #返回绝对路径
os.path.basename(path) #返回文件名
os.path.commonprefix(list) #返回多个路径中,所有path共有的最长的路径。
os.path.dirname(path) #返回文件路径
os.path.exists(path) #路径存在则返回True,路径损坏返回False
os.path.lexists #路径存在则返回True,路径损坏也返回True
os.path.expanduser(path) #把path中包含的"~"和"~user"转换成用户目录
os.path.expandvars(path) #根据环境变量的值替换path中包含的”$name”和”${name}”
os.path.getatime(path) #返回最后一次进入此path的'时间。
os.path.getmtime(path) #返回在此path下最后一次修改的时间。
os.path.getctime(path) #返回path的大小
os.path.getsize(path) #返回文件大小,如果文件不存在就返回错误
os.path.isabs(path) #判断是否为绝对路径
os.path.isfile(path) #判断路径是否为文件

os.path.isdir(path) #判断路径是否为目录
os.path.islink(path) #判断路径是否为链接
os.path.ismount(path) #判断路径是否为挂载点()
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) #把目录和文件名合成一个路径
os.path.normcase(path) #转换path的大小写和斜杠
os.path.normpath(path) #规范path字符串形式
os.path.realpath(path) #返回path的真实路径
os.path.relpath(path[, start]) #从start开始计算相对路径
os.path.samefile(path1, path2) #判断目录或文件是否相同
os.path.sameopenfile(fp1, fp2) #判断fp1和fp2是否指向同一文件
os.path.samestat(stat1, stat2) #判断stat tuple stat1和stat2是否指向同一个文件
os.path.split(path) #把路径分割成dirname和basename,返回一个元组
os.path.splitdrive(path) #一般用在windows下,返回驱动器名和路径组成的元组
os.path.splitext(path) #分割路径,返回路径名和文件扩展名的元组
os.path.splitunc(path) #把路径分割为加载点与文件
Python遍历文件夹如何利用3
1. 基本实现
[root@localhost ~]# cat dirfile.py
import os
path=\'/tmp\'for dirpath,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(path): for file in filenames:
fullpath=os.path.join(dirpath,file) print fullpath
执行结果如下:
[root@localhost ~]# python dirfile.py
/tmp/yum.log/tmp/pulse-3QSA3BbwpQ49/pid/tmp/pulse-3QSA3BbwpQ49/native/tmp/.esd-0/socket
2. 在上例的基础上传递参数
import os,sys
path=sys.argv[1]for dirpath,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(path): for file in filenames:
fullpath=os.path.join(dirpath,file) print fullpath
执行方式为:[root@localhost ~]# python dirfile.py /tmp
在这里,sys.argv[1]是接受参数,也可以定义sys.argv[2]接受第二个参数
3. 如何用函数实现
import os,sys
path=\'/tmp\'def paths(path):
path_collection=[] for dirpath,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(path): for file in filenames:
fullpath=os.path.join(dirpath,file)
path_collection.append(fullpath) return path_collectionfor file in paths(path): print file
【Python遍历文件夹如何利用】相关文章:
如何利用穴道减肥09-13
如何利用风水赚钱09-15
如何利用经期减肥09-21
python简介08-16
如何利用太极气功减肥09-12
如何利用风水理论选址09-12
产后如何利用瑜珈减肥09-15
如何利用“看电视”减肥09-15
如何利用风水提升住宅09-12
python是什么06-14